Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumoto, Toshinori; Kawabe, Ryuhei*; Iwasawa, Yuzuru; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 178, p.109348_1 - 109348_13, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency extended the applicability of their fuel-coolant interaction analysis code JASMINE to simulate the relevant phenomena of molten core in a severe accident. In order to evaluate the total coolability, it is necessary to know the mass fraction of particle, agglomerated and cake debris and the final geometry at the cavity bottom. An agglomeration model that considers the fusion of hot particles on the cavity floor was implemented in the JASMINE code. Another improvement is introduction of the melt spreading model based on the shallow water equation with consideration of crust formation at the melt surface. For optimization of adjusting parameters, we referred data from the agglomeration experiment DEFOR-A and the under-water spreading experiment PULiMS conducted by KTH in Sweden. The JASMINE analyses reproduced the most of the experimental results well with the common parameter set, suggesting that the primary phenomena are appropriately modelled.
Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Takumi; Madokoro, Hiroshi; Nagae, Yuji
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 173, p.109129_1 - 109129_15, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ono, Ayako; Kurihara, Akikazu; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Ito, Masami*; Nakane, Shigeru*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/04
The water experiment apparatus simulating the thermal hydraulics in a reactor vessel under operating the decay heat removal systems (DHRSs) was fabricated. The theoretical evaluation for similarity and results of basic experiments show applicability for a scale model experiment of a sodium-cooled fast reactor. This paper, moreover, describes the results of flow visualization experiment under operating a dipped-type passive DHX, which is planned to be installed in both a loop type reactor and pool type reactor, and the calculation results using FLUENT comparing with the result of water experiment.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 96, p.137 - 147, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:43.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)After Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster by TEPCO, a cooling system to prevent core damage became more important from the perspective of defense in depth. Therefore, a new, highly efficient RCCS with passive safety features without a requirement for electricity and mechanical drive is proposed. Employing the air as the working fluid and the ambient air as the ultimate heat sink, the new RCCS design strongly reduces the possibility of losing the heat sink for decay heat removal. The RCCS can always stably and passively remove a part of the released heat at the rated operation and the decay heat after reactor shutdown. Specifically, emergency power generators are not necessary and the decay heat can be passively removed for a long time, even forever if the heat removal capacity of the RCCS is sufficient. We can also define the experimental conditions on radiation and natural convection for the scale-down heat removal test facility.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Matsumoto, Tatsuya*; Morita, Koji*
Proceedings of 2016 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2016) (CD-ROM), p.1250 - 1257, 2016/04
After Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster by TEPCO, a cooling system to prevent core damage became more important from the perspective of defense in depth. Therefore, a new, highly efficient RCCS with passive safety features without a requirement for electricity and mechanical drive is proposed. Employing the air as the working fluid and the ambient air as the ultimate heat sink, the new RCCS design strongly reduces the possibility of losing the heat sink for decay heat removal. The RCCS can always stably and passively remove a part of the released heat at the rated operation and the decay heat after reactor shutdown. Specifically, emergency power generators are not necessary and the decay heat can be passively removed for a long time, even forever if the heat removal capacity of the RCCS is sufficient. We can also define the experimental conditions on radiation and natural convection for the scale-down heat removal test facility.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Hu, R.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 77, p.165 - 171, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new, highly efficient reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS) with passive safety features without a requirement for electricity and mechanical drive is proposed. The RCCS design consists of continuous closed regions; one is an ex-reactor pressure vessel (RPV) region and another is a cooling region having heat transfer area to ambient air assumed at 40 ( C). The RCCS uses a novel shape to efficiently remove the heat released from the RPV with radiation and natural convection. Employing the air as the working fluid and the ambient air as the ultimate heat sink, the new RCCS design strongly reduces the possibility of losing the heat sink for decay heat removal.
C). The RCCS uses a novel shape to efficiently remove the heat released from the RPV with radiation and natural convection. Employing the air as the working fluid and the ambient air as the ultimate heat sink, the new RCCS design strongly reduces the possibility of losing the heat sink for decay heat removal.
Moriyama, Kiyofumi; Nakamura, Hideo; Maruyama, Yu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 236(19-21), p.2010 - 2025, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A computer code JASMINE-pre was developed for the prediction of premixing conditions of fuel-coolant interactions and the debris bed formation behavior relevant to severe accidents of light water reactors. JASMINE-pre consists of three melt component models: melt jet, melt particles and melt pool, coupled with a two-phase flow model derived from the ACE-3D code developed at JAERI. Simulations of the FARO corium quenching experiments with a saturated water pool and with a subcooled water pool were performed with JASMINE-pre and 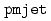 . JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
. JASMINE-pre reproduced the pressurization and fragmentation behaviors observed in the experiments with a reasonable accuracy. The results by pmjet showed qualitatively the same trend with JASMINE-pre in the fragmentation behavior.
Terasaki, Hidenori*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; Okada, Taku; Maeda, Makoto*; Sato, Jin*; Kubo, Tomoaki*; Kasai, Shizu*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 190(1-2), p.93 - 101, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:68.57(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The Fe-FeS melt is thought to be the major candidate of the outer core material. Its viscosity is one of the most important physical properties to study the dynamics of the convection in the outer core. We performed the in situ viscosity measurement of the Fe-FeS melt under high pressure using X-ray radiography falling sphere method with a novel sample assembly. Viscosity was measures in the temperature, pressure, and compositional conditions of 1233-1923 K, 1.5-6.9 GPa, and Fe-Fe 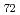 S
S 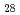 (wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm
(wt %), respectively. The viscosity coefficients obtained by 17 measurements change systematically in the range of 0.008-0.036 Pa s. An activation energy of the viscous flow, 30 kJ/mol, and the activation volume, 1.5 cm  /mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe
/mol, are determined as the temperature and pressure dependence, and the viscosity of the Fe 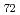 S
S 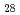 melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
melt is found to be smaller than that of the Fe melt by 15 %. These tendencies can be well correlated with the structural variation of the Fe-FeS melt.
Maruyama, Yu; Sugimoto, Jun
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 36(10), p.914 - 922, 1999/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Jun; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro*; Yamano, Norihiro; Hidaka, Akihide; Maruyama, Yu; Uetsuka, Hiroshi; Fuketa, Toyoshi; Nakamura, Takehiko; Soda, Kunihisa; Katanishi, Shoji*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 39(2), p.123 - 134, 1997/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sugimoto, Jun; Uetsuka, Hiroshi; Hidaka, Akihide; Maruyama, Yu; Yamano, N.; Hashimoto, Kazuichiro
Thermophysical Properties 17 (17th Japan Symp. 1996), 0, p.163 - 166, 1996/00
no abstracts in English
Ishigami, Tsutomu; Kobayashi, Kensuke
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 35(6), p.549 - 560, 1993/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; *; ; *;
Genshiryoku Kogyo, 32(12), p.17 - 31, 1986/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; *; *
Source Term Evaluation for Accident Conditions, p.733 - 744, 1986/00
no abstracts in English
; *; ; *
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 27(1), p.56 - 65, 1985/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:24.17(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; *
JAERI-M 84-055, 454 Pages, 1984/03
no abstracts in English
; ; Murao, Yoshio; ; ; ; ; ; ; Ueda, Shuzo; et al.
JAERI-M 82-039, 201 Pages, 1982/05
no abstracts in English
*; ;
JAERI-M 9091, 50 Pages, 1980/10
no abstracts in English
; *;
JAERI-M 9090, 34 Pages, 1980/09
no abstracts in English